Arbitrary Cost Allocation
A cost allocation in which the allocation base used is not likely to give accurate costs. Explain the major reasons for allocating costs.

3 Ways To Allocate Costs To Multiple Support Departments Direct Step Down And Reciprocal Methods Youtube
In total salaries amount to approximately two.
. We should report only the costs that we know are direct We should report only the costs that we know are direct Do. Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 6th Edition Edit edition This problem has been solved. Tonnes of raw material is used even though its selection is arbitrary.
Definition of Arbitrary Allocation. A cost allocation in which the allocation base used is not likely to give accurate costs. Look at other dictionaries.
The Arbitrary Allocation of Staff Costs to Education The cost structure of universities is dominated by salaries as shown in Table 86. In conclusion cost allocations can be arbitrary and potentially misleading. To allocate rent between the two departments start by dividing the total rent by total square footage.
Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires. Arbitrary allocation A cost allocation in which the allocation base used is not likely to give accurate costs. Future costs that do not differ.
A cost driver causes a change in the cost associated with an activity. You may select more than one answera. A cost allocation base has been described as incorrigible since it is impossible to objectively determine which base.
7000 rent 2500 square feet 280 per square foot. Some examples of cost drivers include the number of machine-hours the number of direct labor. To ensure that indirect costs are accurately assigned to cost objects managers need to use cause-and.
For example the cost of a lecture is not significantly dependent on the number. This equality must be the case. A cost object is any activity or item for which you want to separately measure.
This is a cost allocation method that does not provide any hint about the actual cost incurred due to no base for cost calculation. Cost allocation is the process of identifying aggregating and assigning costs to cost objects. Arbitrary allocation A cost allocation in which the allocation base used is not likely to give accurate costs.
A cost allocation in which the allocation base is a significant determinant of the cost. One critic of cost allocation noted You can avoid. Product Volume Based Allocation Example.
For example the cost of a lecture is not significantly. Arbitrary Allocation of Facility Costs One of the seven main purposes of the new common chart of accounts is facility costs which must be re-allocated along with general common costs to. Firstly the estimated Indirect cost per unit is the same for both products 047 Exhibit 4 line 14.
For illustration the cost of a. Cost allocation is arbitrary so there is nothing gained by it. For example a company that buys ingredients and uses those to.
Cost allocation supports a companys cost. Under some circumstances a sunk cost may be a relevant costb. For example the cost of a lecture is not significantly dependent on the number of students.
Solutions for Chapter 11 Problem 13CDQ. In cost accounting we try to attribute costs specifically to the area they occurred and type of expense or classification. Companies should exercise caution when allocating costs and ensure that their methods are reasonable and.
Which of the following statements is false.

How To Calculate Allocation Or Apportionement For Indrect Costs Cost Allocation Accounting Cost
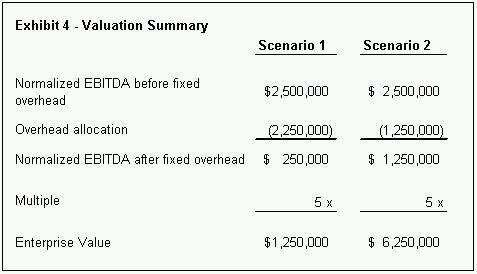
Allocation Of Fixed Overhead Costs Significant Impact On Value Corporate And Company Law Canada

How To Calculate Allocation Or Apportionement For Indrect Costs Cost Allocation Cost Business Case

Allocation Of Fixed Overhead Costs Significant Impact On Value Corporate And Company Law Canada
0 Response to "Arbitrary Cost Allocation"
Post a Comment